Mesothelioma - malignant
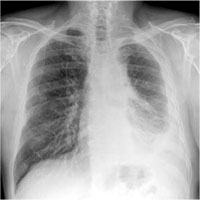
Malignant mesothelioma is an uncommon cancerous tumor of the lining of the lung and chest cavity (pleura) or lining of the abdomen (peritoneum). It is due to long-term asbestos exposure.
Long-term exposure to asbestos -- a fire-resistant material -- is the biggest risk factor. Asbestos was once commonly found in insulation, ceiling and roofing vinyls, cement, and automotive brake materials. Although many asbestos workers smoked, experts do not believe smoking itself is a cause of this condition.
Malignant mesothelioma affects men more often than women. The average age at diagnosis is 60. Most people seem to develop the condition about 30 years after being in contact with the asbestos.
Symptoms may not appear until 20 to 50 years or longer after exposure to asbestos, and may include:
- Abdominal bloating
- Abdominal pain
- Chest pain, especially when taking a deep breath
- Cough
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Weight loss
 |
| Mesothelioma - malignant |